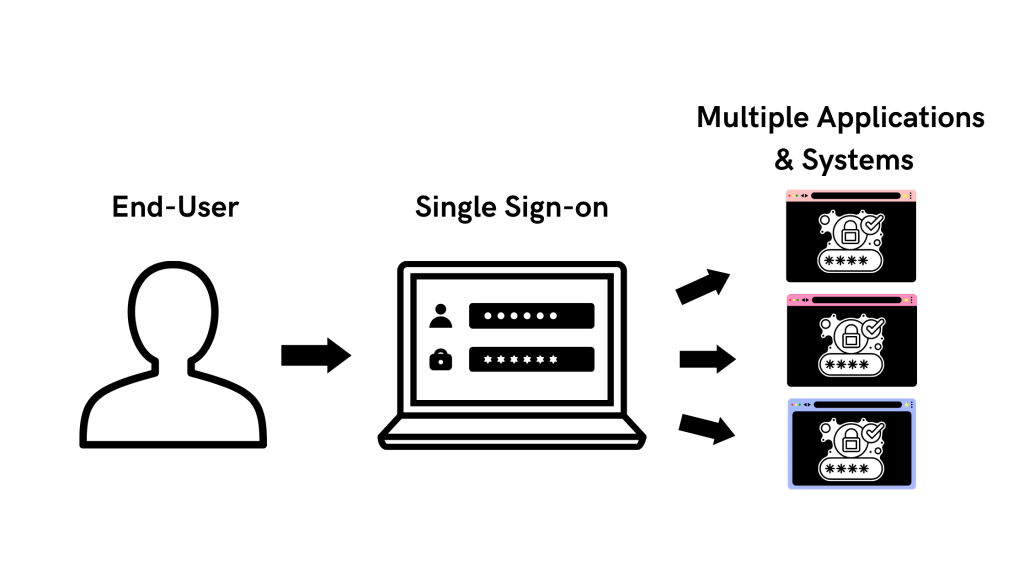
Individuals and organizations rely heavily on various online platforms and services, the need for a secure and convenient way to access these resources is paramount. This is where SSO Single Sign-On comes into play. SSO Single Sign-On is a powerful authentication method that allows users to securely sign in to multiple applications and platforms using just one set of credentials. In this article, we will explore the benefits of SSO Single Sign-On, its implementation, and how it enhances security while streamlining the user experience.
Understanding SSO Single Sign-On
What is SSO Single Sign-On? SSO Single Sign-On is an authentication process that enables users to access multiple applications and platforms using a single set of login credentials. With SSO Single Sign-On, users only need to remember one username and password, eliminating the hassle of managing multiple credentials for different services. This not only saves time but also enhances convenience for users.
How does SSO Single Sign-On work? SSO Single Sign-On works by establishing a trust relationship between an identity provider (IdP) and the various service providers (SPs). When a user attempts to access a service, the IdP verifies the user’s identity and provides a token to the SP, which grants the user access without requiring additional authentication. This seamless process simplifies the login experience and eliminates the need for users to repeatedly enter their credentials.
Benefits of SSO Single Sign-On
Enhanced Security: One of the key advantages of SSO Single Sign-On is its ability to enhance security. By consolidating login credentials into a single set, users are less likely to resort to weak passwords or reuse passwords across multiple platforms. This reduces the risk of password-related security breaches. Additionally, SSO Single Sign-On allows for stronger authentication methods, such as two-factor authentication, further bolstering security without requiring multiple accounts.
Streamlined User Experience: With SSO Single Sign-On, users no longer have to remember and enter multiple sets of login credentials. This significantly reduces the login friction and streamlines the user experience. Users can seamlessly navigate between different applications and platforms without the need for repetitive logins. This convenience not only saves time but also improves productivity.
Centralized Access Management: SSO Single Sign-On provides organizations with centralized access management capabilities. Administrators can easily control user access to various applications and platforms from a centralized dashboard. This simplifies user provisioning and deprovisioning, ensuring that employees have timely access to the resources they need while maintaining security and compliance.
Cost and Time Savings: Implementing SSO Single Sign-On can lead to cost and time savings for organizations. By reducing the number of password-related support requests, IT teams can focus on more strategic initiatives. Additionally, the streamlined login experience reduces the time spent by employees on authentication, leading to increased productivity and efficiency.
Implementing SSO Single Sign-On
To implement SSO Single Sign-On, organizations need to follow a few key steps:
- Evaluate SSO Solutions: Begin by evaluating various SSO solutions available in the market. Consider factors such as compatibility with existing systems, scalability, security features, and ease of integration.
- Choose an Identity Provider: Select an identity provider that aligns with your organization’s requirements. The identity provider will be responsible for authenticating users and issuing tokens for accessing service providers. Office 365 and Google Workspace are usually the best, most prolific IdP sources to use.
- Configure Service Providers: Configure the service providers that you want to integrate with SSO Single Sign-On. This involves establishing trust relationships between the identity provider and the service providers.
- User Provisioning and Deprovisioning: Implement a user provisioning and deprovisioning process to ensure that users have the necessary access to the applications and platforms they require. This process should be integrated with the SSO Single Sign-On solution to maintain centralized access management.
- Test and Monitor: Thoroughly test the SSO Single Sign-On implementation to ensure its functionality and security. Regularly monitor the system to identify and address any potential issues or vulnerabilities.
Best Practices for SSO Single Sign-On Implementation
When implementing SSO Single Sign-On, it is essential to follow best practices to maximize security and usability:
- Strong Authentication: Implement strong authentication methods such as two-factor authentication or biometric authentication to enhance security.
- Regular Auditing: Conduct regular audits of user access rights and permissions to ensure compliance and detect any unauthorized access.
- User Education: Educate users about the benefits of SSO Single Sign-On and best practices for password management to promote secure behavior.
- Continuous Monitoring: Implement a robust monitoring system to detect and respond to any suspicious activities or potential security threats.
- Regular Updates: Keep the SSO Single Sign-On solution and all integrated applications up to date with the latest security patches and updates.
Remember, security should never be compromised, and SSO Single Sign-On provides a robust solution to protect user identities and streamline access to applications and platforms. Embrace the power of SSO Single Sign-On and enjoy the benefits of enhanced security and convenience.